All the Basic Specifications You Need to Know for Your Videos
![]() Rocío Cortázar · 12 Feb, 2026 · Diseño Gráfico · 7 min
Rocío Cortázar · 12 Feb, 2026 · Diseño Gráfico · 7 min
In the digital age we live in, video has become a fundamental part of our daily life. From entertainment to education and communication, video is the king. However, it is easy to feel overwhelmed by all the different specifications for videos that are part of this world and choose what is best for each case, as they can make a difference in the quality and performance of your videos.
As we already have an article that talks about All the image formats you need to know and what to use them for, today we will look at the most basic specifications so you can maximize the possibilities that this audiovisual tool offers.
The video format is a term that is used very broadly. It can include various specifications that address the quality of the video, the resolution, the size, etc. Let’s break down the format and delve a little into the correct terms and their meaning so you understand them perfectly and know which ones to pay attention to.
File Formats
The file type is one of the main video specifications and is identified by the extension at the end of the file name, for example, mywonderfulvideo.mp4. Some of the most common include MP4, AVI, MOV, MKV, but there are many more. Each has its own characteristics and advantages, so it’s important to choose the right one according to your specific needs. Today we will see the most common and versatile ones:
- MP4
This is the most common and popular video file type. It is widely compatible and works on different tools, platforms, and devices, making it ideal for sharing and playing videos in different places. MP4 files are lightweight and therefore more compressed. They are ideal for use on social media and other cases where large-scale projections are not needed.
- AVI
It is one of the oldest and most universally accepted standard video formats. They can be played on a wide range of players and are known for their high quality, so .AVI file sizes tend to be large, which can affect the ease of sharing and storing videos.
- MOV
Developed by Apple, the MOV format is widely used on iOS and macOS devices, making it a great choice for users of these operating systems. It is a native Quicktime format, so if you install this software on your PC, you can also play it. It is less compressed than MP4, so it requires more processing power to handle, but the advantage is that videos tend to be of higher quality. It is a popular choice among professionals such as video editors because the quality can be maintained when editing and adjusting the image.
- MKV
Its full name is Matroska, like the traditional Russian dolls. And this is not by chance, but because of its ability to store multiple video, audio, and subtitle tracks in a single file. It is a professional video format that provides very good audio and video quality in little space. It is ideal for distributing multimedia content with multiple playback options.
When choosing a file format for your videos, consider the quality, compatibility, and file size to ensure an optimal experience for your viewers.
Video Orientation and Aspect
The orientation and aspect of the video are important video specifications to consider when creating visual content. The orientation of the video simply defines which side of the video frame is wider, that is, whether the video is horizontal (landscape), which is wider, or vertical (portrait), which is taller. The aspect of the video refers to the ratio between the width and height of the video frame, also known as the aspect ratio.
- Orientation
The orientation of the video can affect how content is perceived and consumed. Videos in horizontal mode are ideal for panoramic and landscape scenes, while videos in vertical mode are more suitable for portraits and content focused on people or vertical objects.
- Aspect
The aspect ratio of a video is generally expressed as a ratio between the width and the height of the video. The most well-known is 16:9. It indicates that for every 16 pixels wide, there are 9 pixels high. So any 16:9 video can be 1920×1080 px, 960×540 px, 2400×1350 px, etc. But there are also other very popular ones like 1:1, 4:3, or 21:9. The 16:9 aspect ratio is the most used on most devices and platforms, as it provides a balance between large-screen viewing and mobile device viewing. The aspect ratio can also be used to identify orientation. Therefore, 16:9 is used for landscape, 9:16 for portrait, and 1:1 for the square video frame.
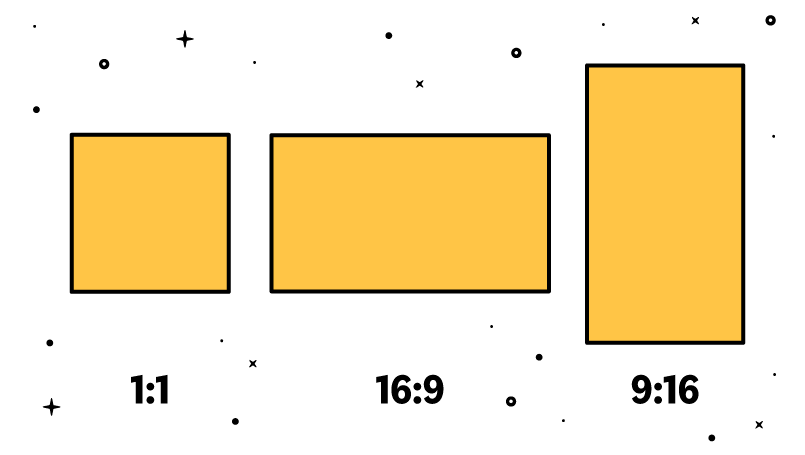
When considering the orientation and aspect of your videos, it is important to think about how and where the content will be viewed and choose the option that best suits your needs and target audience.
Resolution
With resolution, it’s all about pixels; it basically defines the physical dimensions of a video. Just like with images, it describes the width and height of the video in pixels. One of the most common resolutions is 1920×1080. It is also known as Full HD, or 1080p for friends. Similarly, 1280×720 px is known as 720p.
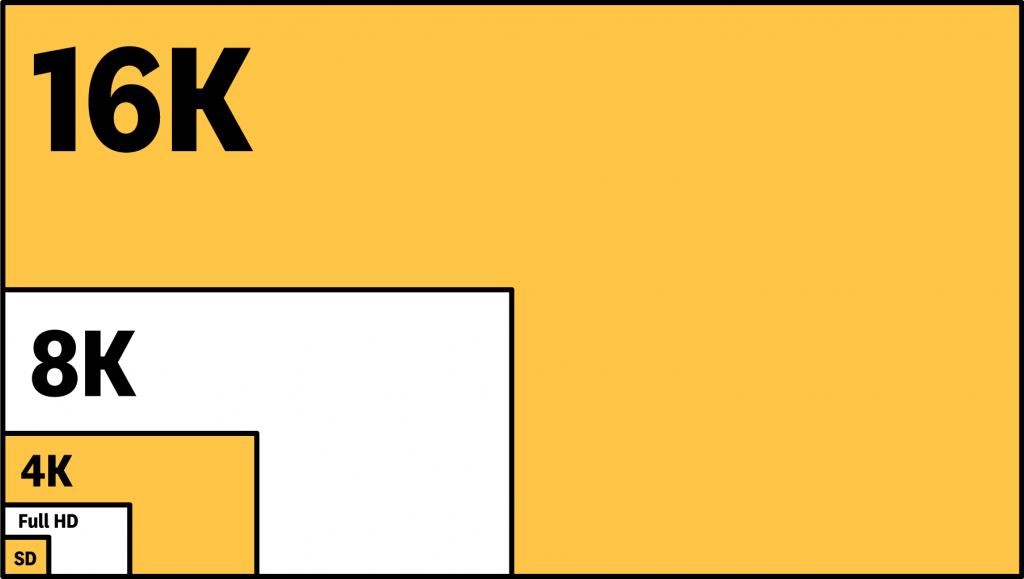
Another common resolution you are probably familiar with is 4K. As expected, 4K means 4 thousand, because it has nearly 4000 pixels wide. Although if we want to get technical, there are two types of 4K; one is the “true” DCI 4K, and then there’s its more common counterpart, 4K UHD. DCI 4K really has the 4 thousand pixels as it has a resolution of 4096x2160px. However, 4K UHD has 3840×2160px, so it doesn’t quite reach 4000 px, making it a kind of “fake” 4K, but it is more common as it fits the aforementioned 16:9 aspect ratio.
The most well-known and used resolutions are:
- 720p HD – 1280×720 px
When sharing videos on social media or making video calls from mobile devices, 720p is a practical choice. It maintains a good balance between quality and data efficiency, catering to a diverse audience with varying internet speeds.
- 1080p Full HD – 1920×1080 px
For content creators on YouTube or online educators. This resolution achieves a good balance, offering clear images suitable for various devices, ensuring a quality viewing experience for your audience.
- 4K UHD – 3840×2160 px
For movies and clips that will be streamed on televisions. Many original Netflix series and movies are available in 4K UHD for subscribers with compatible devices, offering a cinematic experience at home. Companies presenting high-end products, such as the latest smartphones or cameras, can use 4K UHD for detailed presentations.
- 4K DCI – 4096×2160 px
Movies released in theaters often use 4K DCI for a cinematic experience on large screens. It offers a slightly wider format.
What do the acronyms mean?
You may have noticed that there are several acronyms related to resolution. Let’s look at the most common ones:
- HD and Full HD
High Definition. It refers to a standard video resolution that provides greater clarity and detail than standard definition SD of 480p. This definition refers to any video with a resolution of at least 720 pixels in height, but as mentioned before, the most common HD resolution is 1920×1080 pixels, also known as 1080p and Full HD. This standard significantly enhances the visual experience by offering sharper images and more vibrant colors.
- UHD
Ultra High Definition. It represents a resolution higher than HD. The most common UHD resolution is 4K at 3840×2160 pixels, but we also have 8K (7680×4320) and 16K (15360 × 8640). UHD 4K offers four times more pixels than HD, hence its name, resulting in a more detailed and immersive viewing experience. It is widely used in modern televisions, monitors, and content production to enhance visual quality.
- DCI
Digital Cinema Initiatives. It is a standard for digital cinema projection, mainly used in movie theaters. While HD and UHD are aimed at consumer screens, DCI specifies resolutions and technical standards for digital cinema projectors. The two main DCI resolutions are 2K (2048×1080 pixels) and 4K (4096×2160 pixels).
By understanding these acronyms and standards, you can make informed decisions about the quality and format of your videos to ensure an optimal experience for your viewers.
Frames per second (fps) or Frame Rate
Frames per second (FPS) are a measure of how many frames are displayed in the video per second. In short, the higher the frame rate, the smoother the playback will be, which is especially true for clips with a lot of action. On the other hand, a low frame rate can make the video look choppy or less natural. Most videos are played at 24, 30, or 60 FPS, although some video formats support even higher frame rates for slow-motion effects or high-speed recordings.

- 24 FPS
This is the standard frame rate used in the film industry. It provides a smooth and natural playback that is ideal for movies and narrative content.
- 30 FPS
This is the most commonly used frame rate in online videos and television. It provides smooth and fluid playback that is suitable for most types of content.
- 60 FPS
This frame rate is ideal for high-action content and video games, as it provides extremely smooth playback that can capture even the fastest movements with clarity.
- 120 FPS
It achieves extremely smooth and detailed visual playback, ideal for virtual reality, extreme sports, and high-action content. Its use may require specific hardware and resources, limiting its accessibility to a more professional environment.
Really, FPS is a specification you only need to worry about if you are going to record the content yourself, as it is ideal to set it at the time of recording. For example, if you plan to do slow motion, you should take this into consideration and record that clip with a frame rate of 60fps or higher (depending on how slow you want the slow motion).
Don’t fall into the trap of thinking that the more FPS, the better; it’s important to keep in mind that not all devices are capable of playing videos with such high frame rates. Older or less powerful devices may have difficulty playing videos with frame rates higher than 30 fps, which can result in choppy playback or performance issues.
In any case, as a general rule, if you are using videos for social media or other “more relaxed” uses, you don’t need to pay much attention to this section.
I hope all this info has been useful to you and that the next time you have to record some content, you know what options to choose for your video.




